TOTUM•448 is a unique patented combination of plant extracts, specifically designed to inhibit the storage of fat in the liver and to reduce blood and hepatic triglyceride levels.
Metabolic liver diseases (MASLD and MASH): a global situation of concern
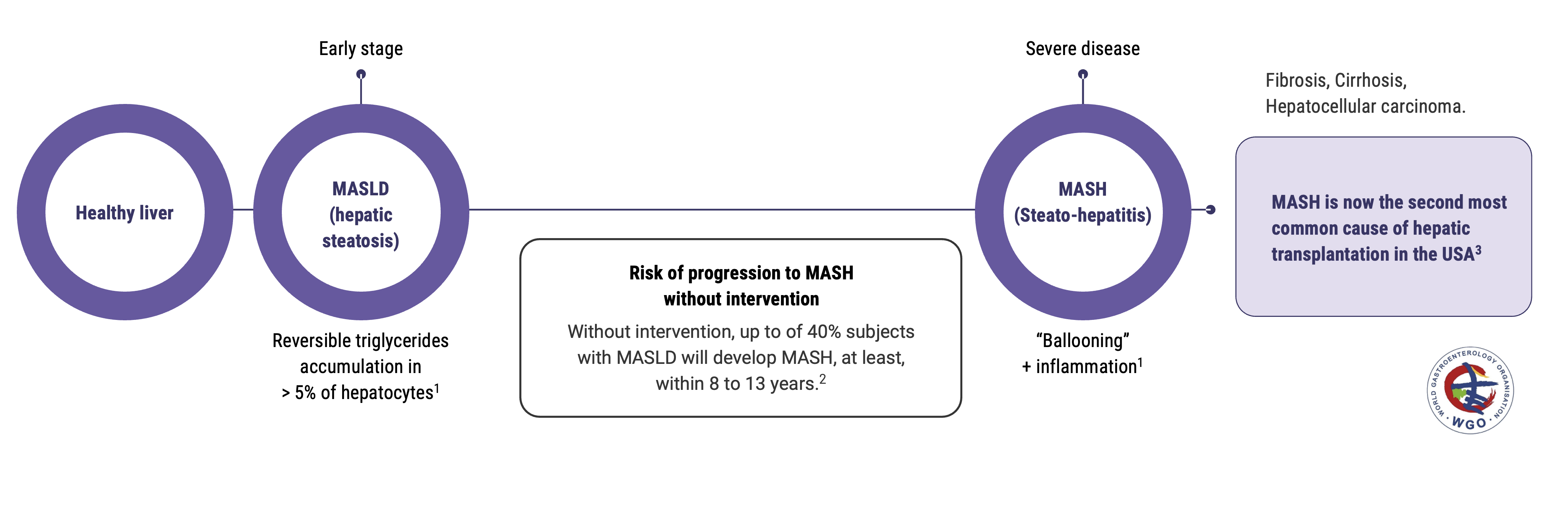
Metabolic hepatic steatosis or MASLD (Metabolic-dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease ) is the first stage of liver metabolic diseases. Steatosis can progress to steato-hepatitis or MASH (Metabolic-dysfunction-Associated Steato-Hepatitis), which strongly increases the risk of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma, and has a very low survival rate. Until June 2023, MASLD and MASH were respectively named NAFLD and NASH.
According to the World Gastroenterology Organisation, the prevalence of metabolic liver diseases has doubled in the last 20 years. Including all stages, they are estimated to impact 25% of the population worldwide, without any therapeutic nor preventive treatment with proven efficacy available to date.
Sources:
– World Gastroenterology Organisation Global Guidelines;
– Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis, 2012;
– Younossi et al. Hepatology, 2016 ; Williams et al., Gastroenterology, 2011;
¹Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis; World Gastroenterology Organization, 2012;
²EASL–EASD–EASO 2016 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol 2016.
Key figures on MASLD and MASH
18% of adults are estimated to have an early stage metabolic liver condition (without fibrosis) in the USA and in the main 5 European countries, i.e. 91 million people.
Source: Elevated LDL, pre-HTA and NAFL preliminary market estimation, AEC Partners, 2020.
Source: Cholankeril G et al. Liver Transplantation for Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in the US: Temporal Trends and Outcomes. Dig Dis Sci. 2017.
12 to 40% in people with MASLD will develop MASH, in the following 8 to 13 years.
Source: EASL-EASD-EASO 2016 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol 2016.
What is TOTUM•448?

The active substance TOTUM•448 is a unique patented combination of plant extracts, designed to reduce hepatic steatosis, a risk condition for MASH.
TOTUM•448 results from preclinical research on metabolic disease models, and aims at inhibiting fat storage in the liver and reducing blood and hepatic triglycerides.
TOTUM•448 preclinical results
Two studies were led in two models of metabolic liver diseases, which mimic the development of the pathology in humans. They showed the efficacy of TOTUM•448 on hepatic steatosis and inflammation, the first two stages of the development of these diseases. They also suggested an improvement in certain markers of fibrosis, observed at later stages.
These promising results were presented at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD), in 2022.
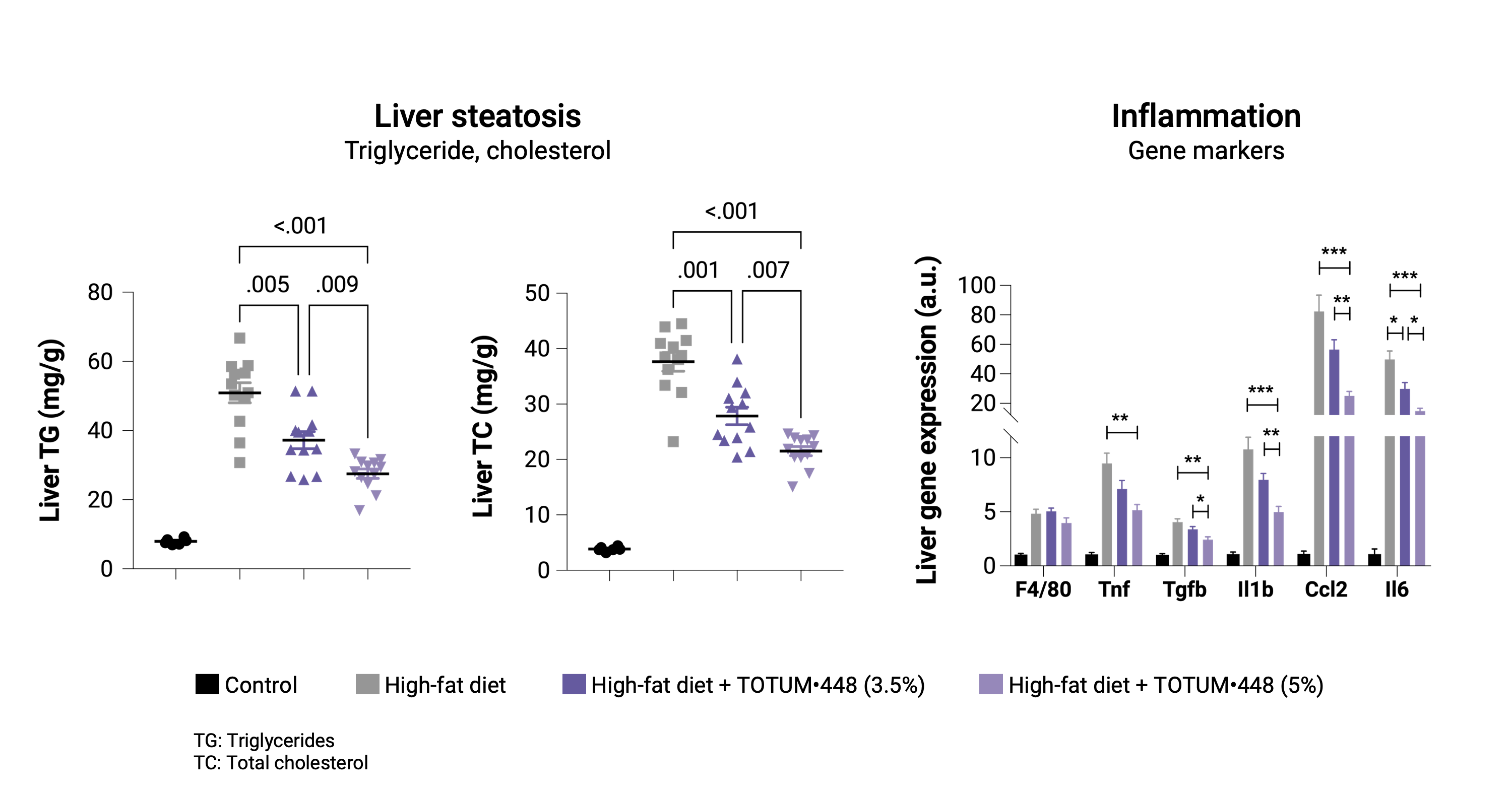
Prevention protocol
In hamsters developing high fat diet-induced MALSD, TOTUM•448 significantly reduced hepatic steatosis with a dose-dependent effect. At the transcriptional level, TOTUM•448 reduced the expression of genes involved in inflammation. Together, these data suggest a preventive effect of TOTUM•448 on steatohepatitis progression.
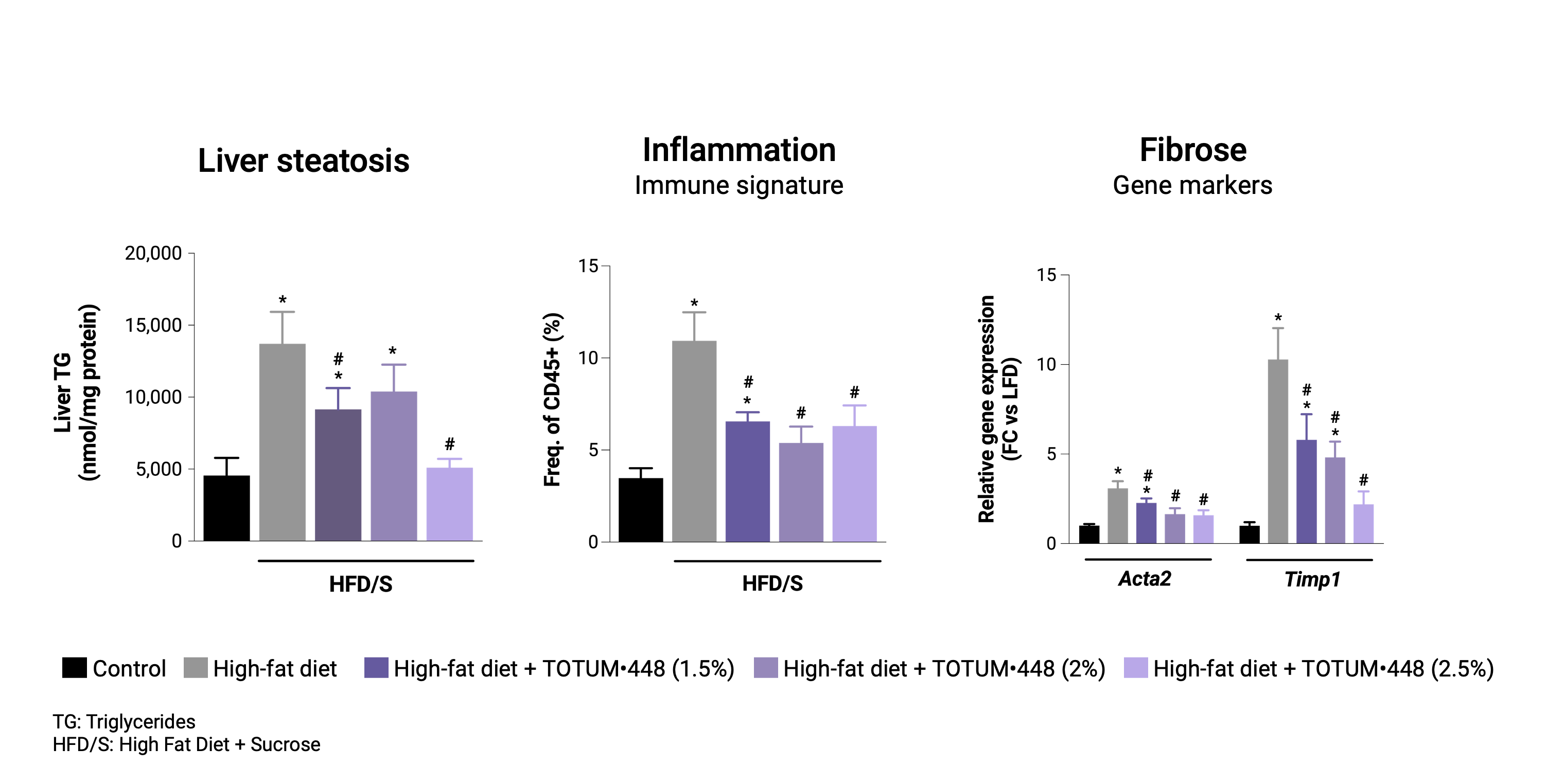
Reversion protocol
In mice with pre-established MASLD, TOTUM•448 reduced liver steatosis, immune markers of liver inflammation, and gene markers of fibrosis, suggesting regression of the steatohepatitis.
Clinical development of TOTUM•448
The TOTUM•448 development strategy was updated to best meet the challenges imposed by an emerging disease for which effective preventive and therapeutic strategies have yet to be developed. It will be based on a clinical efficacy study in healthcare centers and on a clinical bioavailability and mode of action study, which will make it possible to position TOTUM•448 in the best place in the management of MASLD and the MASH.
Intellectual property of TOTUM•448
Valbiotis has adopted a global strategy to protect its intellectual property: patent applications have been filed for TOTUM•448 in 63 countries, including key markets: Europe, USA, Canada, China, Russia, Japan, Brazil and Australia.
Patents have already been issued in 57 countries, including in the USA, Europe (39 countries), China, Russia or Japan, providing a very high level of protection.